---------------------------------------
ATM
Features
ATM Cell
Reference Model
ATM Cell Structure
For all applications
QoS Parameters
Traffic Descriptors
---------------------------------------
ATM is a technology that emphasize on QoS. It guarantees BW, delay and packet loss.
Its a connection-oriented technology, establishes a virtual circuit between the two endpoints before the actual data exchange begins. ATM is a cell relay, packet switching protocol which provides data link layer services that run over Layer 1 links (From wikipedia)
On top of voice and data that FR carries, ATM is a truely integrated services network that can carry voice, video, data and other innovative new services.
Its operating unit is fixed small size packets called cells. This enables the simpler buffer hardware, simpler scheduling and easier to buid high capacity switches. As the cell is small size, there is no much lag time to fill it up before sending and we also have less fragmentation. However, the overhead is also q.high (5B of header for every 48B of payload).
The reference model of ATM consists of 3 planes: Users, control and management planes. And 3 basic layers: ATM Adaptation Later (AAL), ATM layer and physical layer.
User plane take charge of the transferring of user data. Control plane in charge of signaling mechanism for set up, manage and release connection. And Management plane has two part. First, the layer management plane, manage of network resources like BW and buffer in different layers. Second, the plane management plane, to do the coordination of other planes.
AAL, in summery, do the conversion of different data units into blocks of 48B ATM cell, supporting different applications. Next, ATM layer will insert the 5B header to form a complete 53B ATM cell before sending out through physical layer.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
More info from: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/internetworking/technology/handbook/atm.html#wp1020651
The ATM architecture uses a logical model to describe the functionality that it supports. ATM functionality corresponds to the physical layer and part of the data link layer of the OSI reference model.
The ATM reference model is composed of the following planes, which span all layers:
•Control—This plane is responsible for generating and managing signaling requests.
•User—This plane is responsible for managing the transfer of data.
•Management—This plane contains two components:
–Layer management manages layer-specific functions, such as the detection of failures and protocol problems.
–Plane management manages and coordinates functions related to the complete system.
The ATM reference model is composed of the following ATM layers:
•Physical layer—Analogous to the physical layer of the OSI reference model, the ATM physical layer manages the medium-dependent transmission.
•ATM layer—Combined with the ATM adaptation layer, the ATM layer is roughly analogous to the data link layer of the OSI reference model. The ATM layer is responsible for the simultaneous sharing of virtual circuits over a physical link (cell multiplexing) and passing cells through the ATM network (cell relay). To do this, it uses the VPI and VCI information in the header of each ATM cell.
•ATM adaptation layer (AAL)—Combined with the ATM layer, the AAL is roughly analogous to the data link layer of the OSI model. The AAL is responsible for isolating higher-layer protocols from the details of the ATM processes. The adaptation layer prepares user data for conversion into cells and segments the data into 48-byte cell payloads.
Finally, the higher layers residing above the AAL accept user data, arrange it into packets, and hand it to the AAL. Figure 27-7 illustrates the ATM reference model.
Figure 27-7 The ATM Reference Model Relates to the Lowest Two Layers of the OSI Reference Model
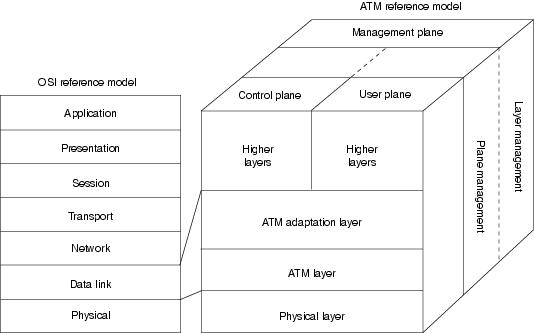
image source from www.cisco.com
----------------------------------------------------------------------
As mentioned right from the start, ATM is a technology that emphasize on QoS. It guarantees BW, delay and packet loss. Therefore, here we look at the QoS Parameters of ATM.
BW
- Peak cell rate (PCR)
- Sustained Cell Rate (SCR)
- Max Burst Size (MBS): relate to Leaky Bucket
- Min Cell rate: whats the use of this?
Delay measured using Cell transfer Delay (CTD). Its the 1 way delay from cell entering network to recieved by destination and is specified by probability density function because its never a constant.
CTD = propagation delay + processing delay + delay at multiplexer and switches + ?
No comments:
Post a Comment